Service providers across the world are gradually rolling out 5G services. The initial focus was primarily on enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB) and Fixed Wireless Access (FWA). However, as 5G matures, 5G Advanced (5.5G) emerges with exciting use cases in Industrial IoT (IIoT), ultra-reliable low-latency communication (uRLLC) and private 5G networks.
As a result, service providers need solutions that can keep up the pace with these rapid changes. At the same time, especially in emerging economies, 4G is still a dominant option. In such cases service providers need a flexible solution that can support 4G while providing a seamless upgrade path towards 5G and beyond.
Tejas Networks RAN solutions are based on software-defined hardware which supports 4G and 5G access, and ensures smooth migration to newer generations with minimal capex and operational overheads. Our integrated access and xhaul (“cross haul” – i.e., front-haul, mid-haul, back-haul in disaggregated RAN architecture) provides multiple transport options depending on the operators’ requirements.
As a result, service providers need solutions that can keep up the pace with these rapid changes. At the same time, especially in emerging economies, 4G is still a dominant option. In such cases service providers need a flexible solution that can support 4G while providing a seamless upgrade path towards 5G and beyond.
Tejas Networks RAN solutions are based on software-defined hardware which supports 4G and 5G access, and ensures smooth migration to newer generations with minimal capex and operational overheads. Our integrated access and xhaul (“cross haul” – i.e., front-haul, mid-haul, back-haul in disaggregated RAN architecture) provides multiple transport options depending on the operators’ requirements.

Key Features

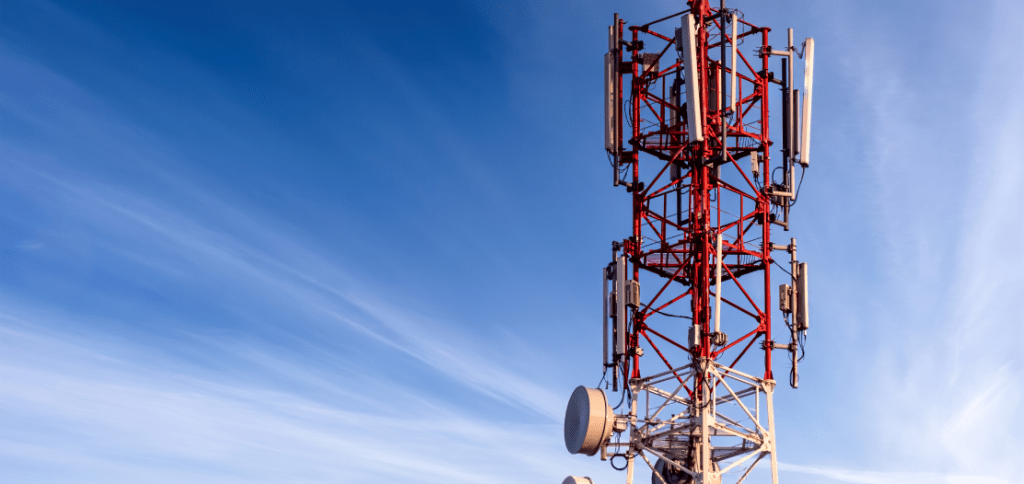
Field Deployed Mobility and FWA Solutions
FDD, TDD – Single and Multiband support in 4G and 5G
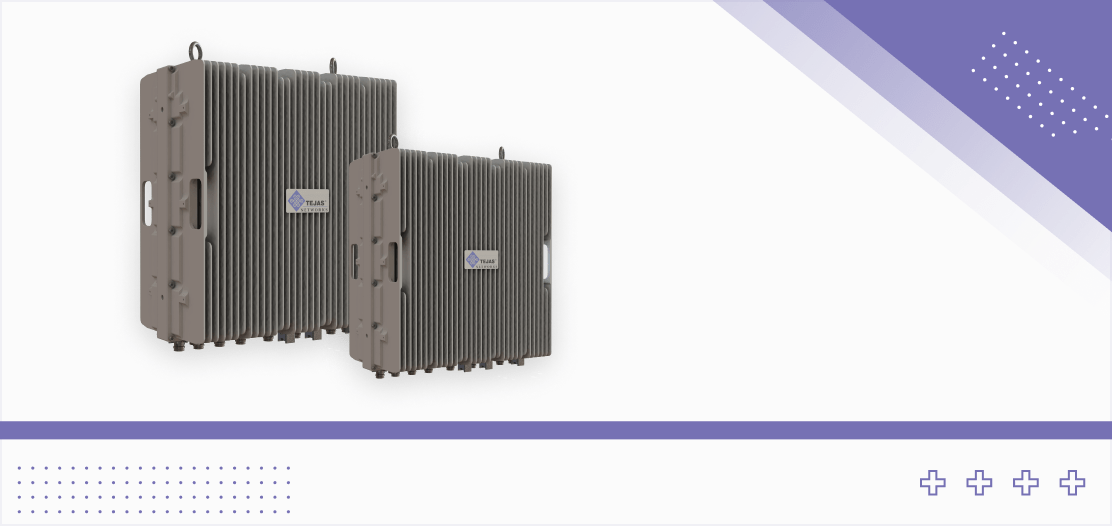
Massive MIMO Radios
Provide superior throughput and reduced latency

Integrated Access and xHaul
Multiple xHaul options – over IP-MPLS, XGS PON, DWDM

Ultra-converged Platforms
Single platform supports 4G and upgradable 5G (including BBU), enabling both FTTx and enterprise data services
Support Network Slicing at Transport Layer
Hard QoS at PTN and OTN makes the transport network fit for network slicing

Enable Seamless Technology Evolution
Software-defined architecture to support constant technology upgradation with optimized TCO
Products and Resources

Radio Access Network
Tejas Radio Access Network Portfolio

Optical Aggregation
Tejas Optical Aggregation Portfolio

Packet Transport Network
Tejas Packet Transport Network Portfolio

Tech Talk – Packet and Optical Networking Technologies for 5G and Beyond: Vasudeva Rao Hundi, Head – PLM

A deep dive into 5G innovations and global telecom ambitions: Kumar Sivarajan, CTO & co-founder, Tejas Networks

